Li Li
February 21, 2025
Why Choose Aluminium Structural Products for Your Building Structure?
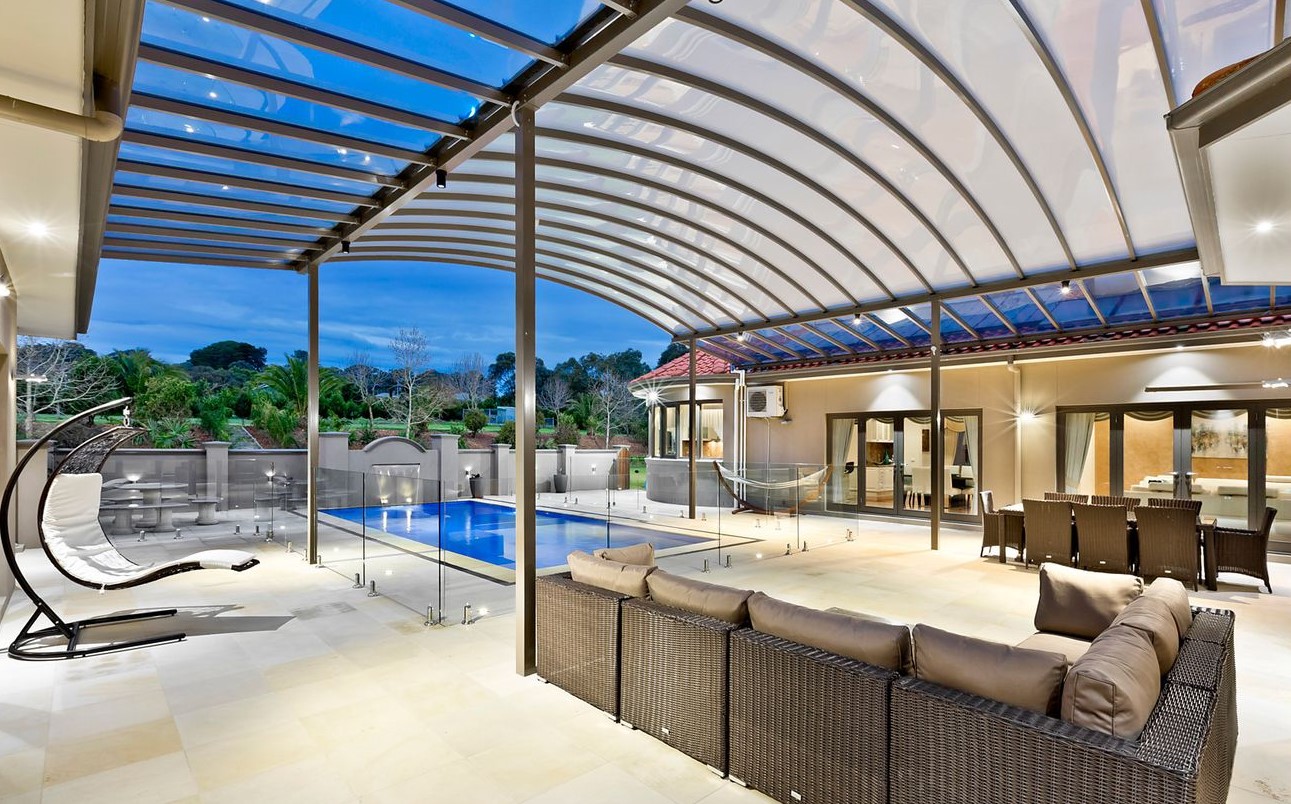
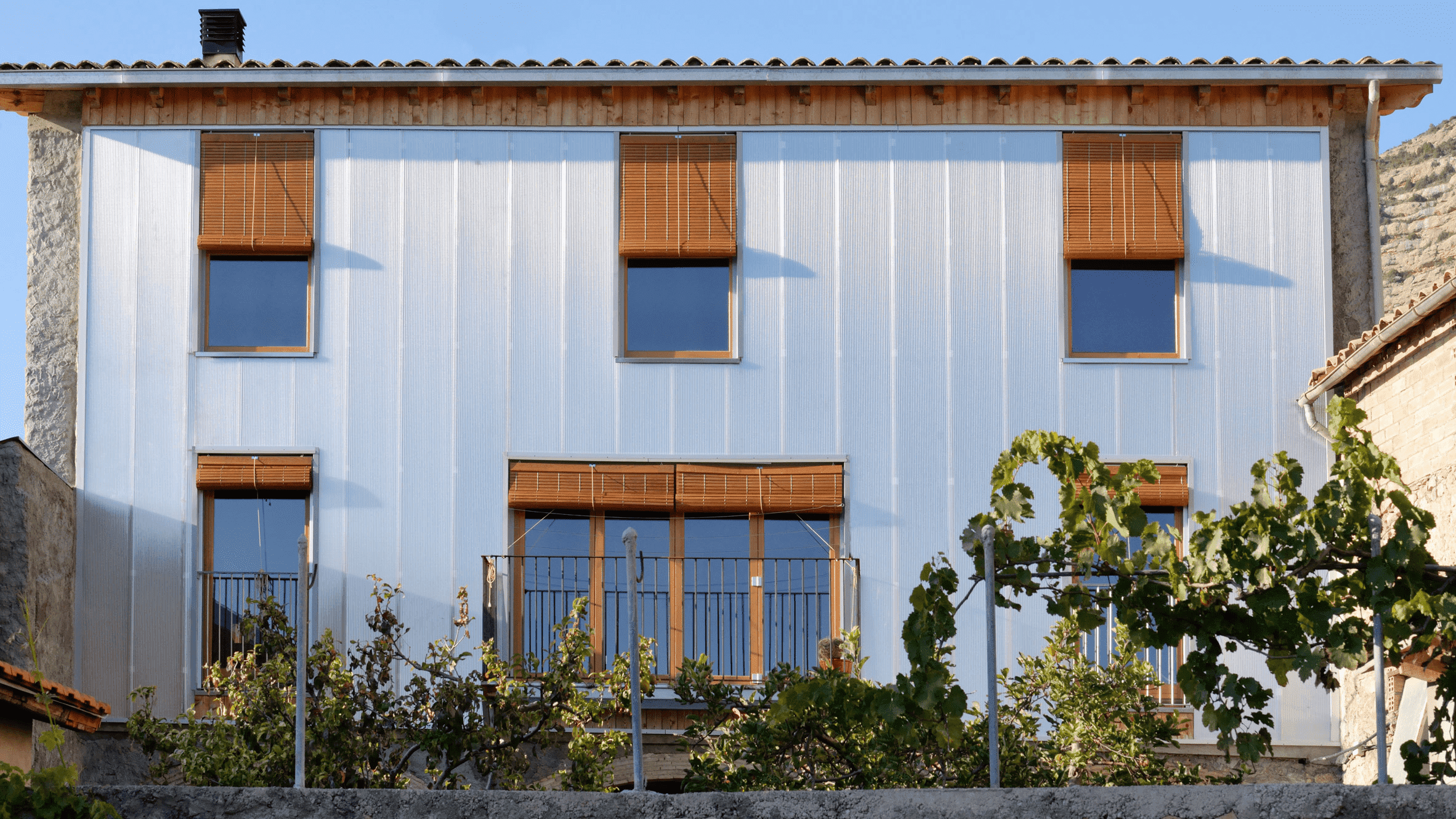
Aluminium is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly conductive metal with excellent malleability and recyclability, making it a versatile material for various industries. It is widely used in transportation (aircraft, cars), packaging (cans, foils), construction (windows, roofing), electrical applications (power lines, cables), and consumer goods (appliances, utensils). Its unique combination of properties, such as durability, low density, and sustainability, ensures its importance in modern technology and everyday life.
________________________________________


Comparison Between Aluminium Alloy and Iron
1. Density and Weight- Aluminium Alloy: Density is about 2.7 g/cm³, making it lightweight and ideal for weight-sensitive applications like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Iron: Density is about 7.87 g/cm³, making it heavier and more suitable for construction and heavy machinery.
- Aluminium Alloy: Moderate strength, but can be enhanced through alloying and heat treatment. Some high-strength aluminium alloys are comparable to steel.
- Iron: Pure iron has low strength, but carbon steel and alloy steel are much stronger, making them ideal for high-load applications.
- Aluminium Alloy: Forms a protective oxide layer, offering excellent corrosion resistance, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
- Iron: Prone to rust and requires protective measures like galvanizing or painting to improve corrosion resistance.
- Aluminium Alloy: Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, often used in heat sinks and electrical components.
- Iron: Poorer thermal and electrical conductivity compared to aluminium.
- Aluminium Alloy: Easy to process, suitable for casting, extrusion, and machining, with lower processing costs.
- Iron: Good workability, but harder grades are more difficult to process, increasing costs.
- Aluminium Alloy: Higher material cost, but lightweight properties reduce transportation and installation expenses.
- Iron: Lower cost and abundant resources, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
- Aluminium Alloy: Widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and packaging industries.
- Iron: Mainly used in construction, bridges, machinery, and heavy equipment.
- Aluminium Alloy: Can be anodized or coated for a modern, sleek appearance.
- Iron: Often used for retro or industrial-style designs.